- Summary
- Table Of Content
- Methodology
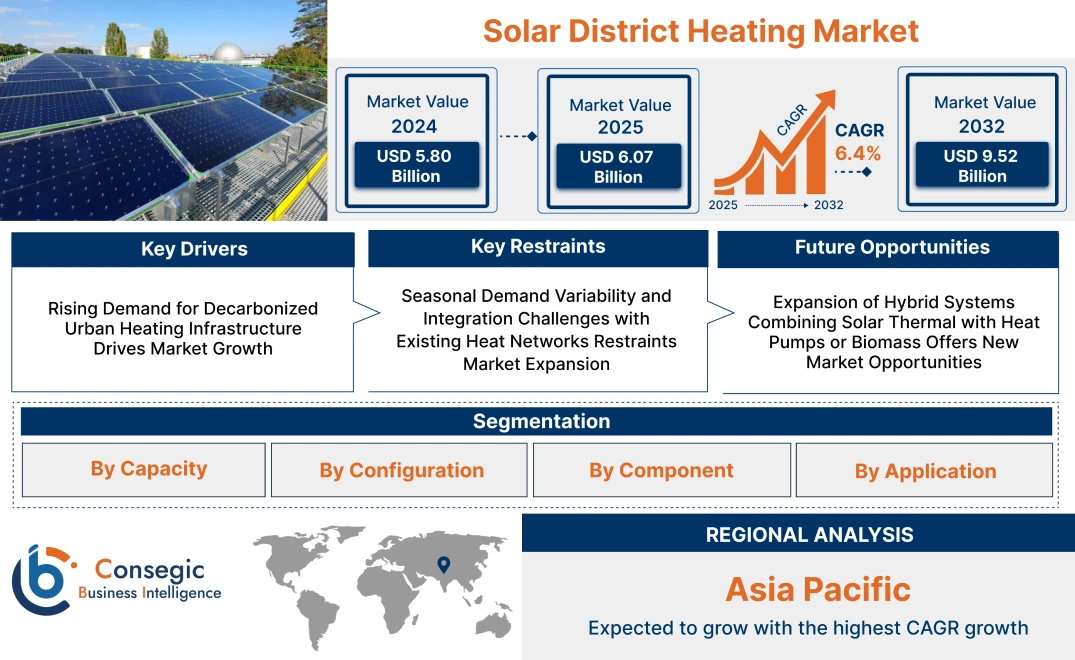
Solar District Heating Market Size:
Solar District Heating Market size is estimated to reach over USD 9.52 Billion by 2032 from a value of USD 5.80 Billion in 2024 and is projected to grow by USD 6.07 Billion in 2025, growing at a CAGR of 6.4% from 2025 to 2032.
Solar District Heating Market Scope & Overview:
Solar district heating is a centralized thermal energy system that employs solar thermal collectors to generate and distribute heat to multiple buildings through a network of insulated pipes. It provides space heating and hot water supply for residential, commercial, and institutional infrastructure by integrating solar energy with thermal storage and backup systems.
Key features include scalability, low maintenance, and compatibility with seasonal heat storage technologies. These systems ensure consistent thermal output, reduce fuel dependency, and support integration with combined heat and power units or biomass boilers. The modular nature of solar collectors allows phased deployment across urban and rural networks.
Municipalities, utility providers, and energy service companies adopt this technology to provide clean and reliable heat to dense urban areas and community developments. Its ability to operate alongside conventional systems while delivering long-term efficiency supports its relevance in low-emission thermal infrastructure planning and sustainable energy management.
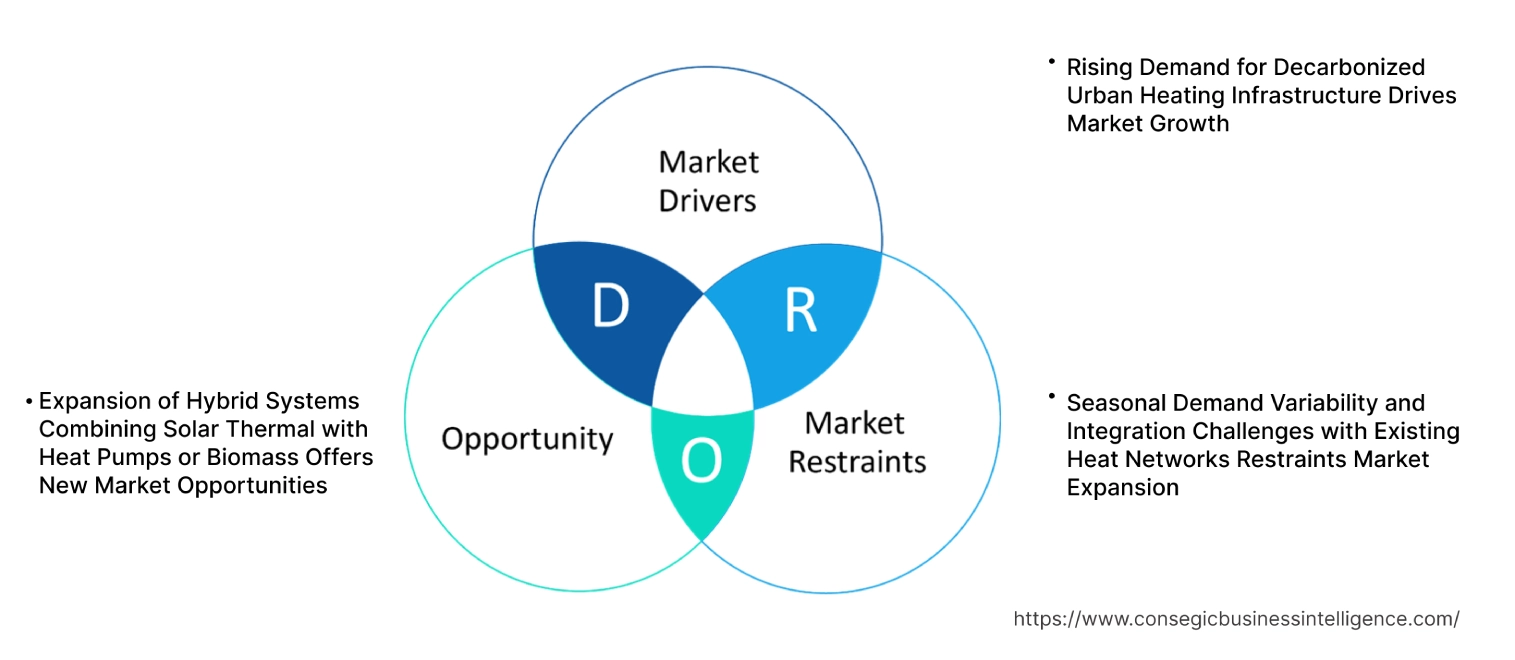
Key Drivers:
Rising Demand for Decarbonized Urban Heating Infrastructure Drives Market Growth
Urban municipalities and national governments are intensifying efforts to transition away from fossil-fuel-based heating as part of broader decarbonization goals. Solar district heating systems offer a scalable, low-emission alternative that supports clean energy targets by reducing long-term dependence on imported fuels. These systems rely on centralized solar thermal collectors to generate heat for entire neighborhoods, industrial zones, or public institutions, significantly lowering carbon emissions. The deployment of large solar collector fields and thermal storage solutions allows for stable heat delivery even during periods of variable sunlight. In addition, these systems align with broader energy independence strategies and contribute to the electrification of urban infrastructure without straining electricity grids. Public sector incentives and municipal climate action plans are accelerating adoption in newly developed and retrofitted city districts. With climate-neutral energy infrastructure becoming a policy priority, the need for these systems continues to grow, fueling solar district heating market expansion.
Key Restraints:
Seasonal Demand Variability and Integration Challenges with Existing Heat Networks Restraints Market Expansion
One of the core technical limitations in this sector is the seasonal mismatch between solar thermal output and end-user heating requirements. In cold climate regions, peak heating demand occurs during winter months when solar irradiance is lowest. While seasonal thermal energy storage mitigates this gap, integrating new solar thermal capacity into legacy heat networks is challenging. Many existing systems are designed around high-temperature fossil-fueled boilers, which are not optimized for low-temperature solar inputs. Converting these networks requires infrastructure upgrades such as temperature-lowering measures, return loop optimization, and control system recalibration. Additionally, variability in solar availability complicates load balancing and requires auxiliary generation sources to maintain continuity. These technical and operational complexities increase costs and prolong project timelines, especially in brownfield applications. As a result, these integration barriers act as a restraint to the solar district heating market growth, particularly in older cities with aging heating infrastructure.
Future Opportunities :
Expansion of Hybrid Systems Combining Solar Thermal with Heat Pumps or Biomass Offers New Market Opportunities
Hybrid heating systems that integrate solar thermal technologies with biomass boilers, large-scale heat pumps, or waste heat recovery are gaining traction across Europe and Asia. These configurations enhance system flexibility and ensure continuous heat delivery regardless of solar availability. During periods of low irradiance or peak demand, auxiliary sources such as biomass or ambient heat via heat pumps fortify solar input, optimizing system performance. This diversified supply approach increases the reliability of thermal networks and enables year-round operation without fossil fuels. Growing requirement for resilient and low-carbon urban energy systems is driving investment in hybrid infrastructure that leverages more than one renewable source. These hybrid models are also more adaptable to district layouts with variable load profiles and seasonal variation. As policymakers and utilities prioritize climate resilience and energy diversification, the development of such systems represents a key growth avenue.
- For instance, in July 2023, Danish renewable energy specialist Aalborg CSP secured an order from the district heating plant Brønderslev Forsyning for a new 1 MW electrical air-to-water heat pump, which integrates with the district heating plant's existing energy system, which consists of a 26,929 m2 solar heating system and two biomass boilers.
These innovations are expected to unlock significant solar district heating market opportunities.
Solar District Heating Market Segmental Analysis :
By Capacity:
Based on capacity, the market is segmented into small-scale, medium-scale, and large-scale.
The small-scale segment held the largest solar district heating market share in 2024.
- Small-scale solar district heating systems are ideal for residential blocks and small commercial buildings in urban and rural setups.
- Their compact design and relatively low installation cost enable quicker adoption across municipalities and community cooperatives.
- These systems are often deployed as pilot projects, serving as an entry point for larger infrastructure investments.
- As per solar district heating market analysis, decentralized energy generation goals and space-constrained locations drive its demand.
The large-scale segment is projected to witness the fastest CAGR during the forecast period.
- Large-scale installations are typically implemented by municipalities and industrial clusters to decarbonize large thermal networks.
- The integration of thermal storage units enhances seasonal performance and reliability in colder climates.
- Market trends highlight that government-funded projects in Europe and Asia are accelerating capacity additions.
- Thus, large-scale systems support district-wide transition to renewable energy, fostering solar district heating market expansion.
By Configuration:
Based on configuration, the solar district heating market is segmented into centralized, decentralized and hybrid systems.
The centralized systems segment dominated the market in 2024.
- Centralized configurations feature large collector fields supplying multiple buildings through a common distribution network.
- These systems offer high operational efficiency, scalable storage options, and centralized control mechanisms.
- Solar district heating market demand from urban infrastructure programs continues to prioritize centralized networks.
- As per the market analysis, cost optimization and thermal energy standardization drive the segment’s dominance.
Hybrid systems are expected to grow at the fastest CAGR during the forecast period.
- Hybrid configurations combine solar thermal with other renewable or backup energy sources like biomass or heat pumps.
- For instance, in October 2024, researchers at the Technical University of Denmark investigated the thermo-economic operation of combined large-scale air-to-water heat pumps and PV-powered district heating systems. The heat pumps were shown to play a dominant role in the fluctuating energy market due to their flexibility, enabling the production and storage of heat in tanks when electricity prices are low, which allows using the stored heat during periods of high electricity prices.
- These systems provide energy security, especially in high-demand periods or low solar irradiance zones.
- Solar district heating market trends show strong deployment in Northern and Eastern Europe, where solar yield variability is higher.
- The segment benefits from flexible integration into legacy heating infrastructure, enabling sustainable urban energy transitions.
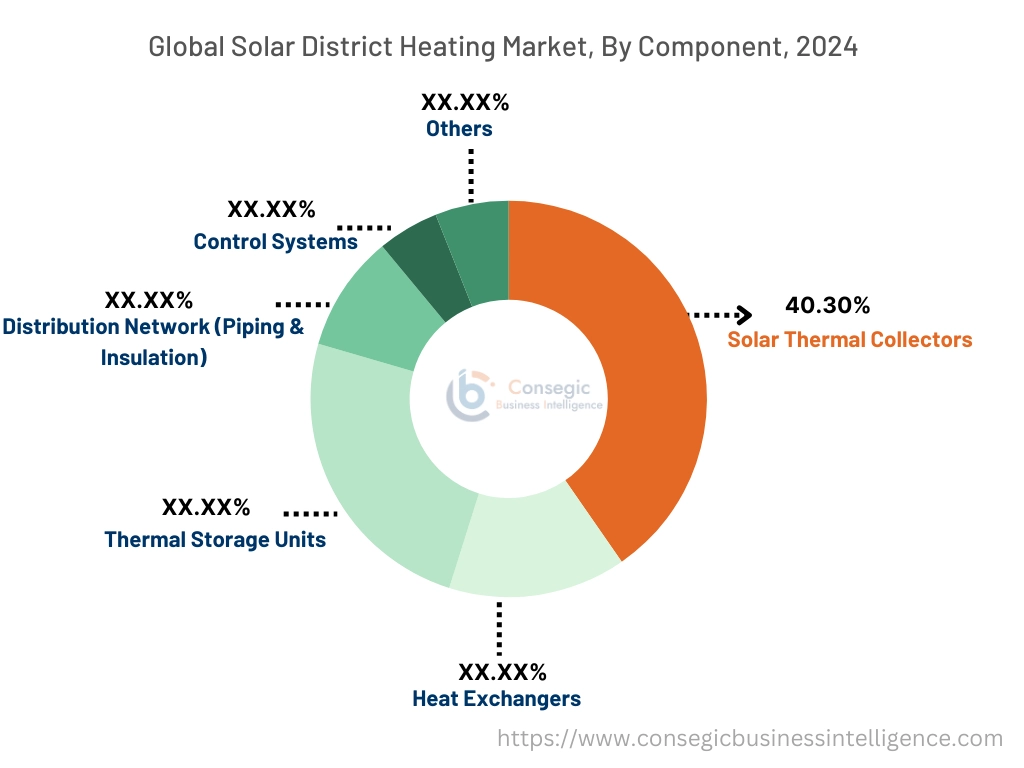
By Component:
Based on component, the market is segmented into solar thermal collectors, heat exchangers, thermal storage units, distribution network (piping & insulation), control systems, and others.
The solar thermal collectors segment held the largest solar district heating market share of 40.30% in 2024.
- Collectors are core to capturing and converting solar radiation into usable heat energy for the district network.
- Technologies include flat plate and evacuated tube collectors, with preference based on climate and efficiency needs.
- Ongoing R&D focuses on improving surface coatings, modular configurations, and cost-to-output ratios.
- As solar district heating market analysis, there is substantial, consistent investment in collector upgrades for higher seasonal efficiency.
Thermal storage units are projected to grow at the fastest CAGR during the forecast period.
- These units store excess heat generated during peak solar hours for use during nights and low irradiance periods.
- Integration with seasonal thermal energy storage (STES) extends system utility and balances load variability.
- Solar district heating market trends suggest rising need for advanced insulation materials and underground storage tanks.
- Growing emphasis on resilience and grid independence accelerates the deployment of thermal storage across both residential and municipal networks.
By Application:
Based on application, the solar district heating market is segmented into residential, commercial, industrial, municipal & district utilities, greenhouse heating, and government institutions.
The residential segment accounted for the largest share in 2024.
- Rising focus on decarbonizing household energy use, particularly for space and water heating, supports residential adoption.
- Multi-apartment and neighborhood-based solar networks are being integrated with smart meters and thermal regulation systems.
- Solar district heating market demand is particularly strong in Europe and China, driven by subsidy-backed housing policies.
- According to segmental analysis, low emissions and cost stability position solar heating as a favorable alternative to fossil-based residential systems.
Greenhouse heating is expected to witness the highest CAGR during the forecast period.
- Controlled environment agriculture is adopting solar thermal systems for sustainable and cost-effective heating.
- Greenhouses benefit from the consistency of thermal energy and the ability to integrate with CO2 fertilization systems.
- Segmental market trends show a strong correlation between horticultural exports and greenhouse adoption.
- As part of broader decarbonization goals, agricultural cooperatives and vertical farms are driving expansion of this segment, reinforcing solar district heating market growth.
Regional Analysis:
The regions covered are North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, the Middle East and Africa, and Latin America.
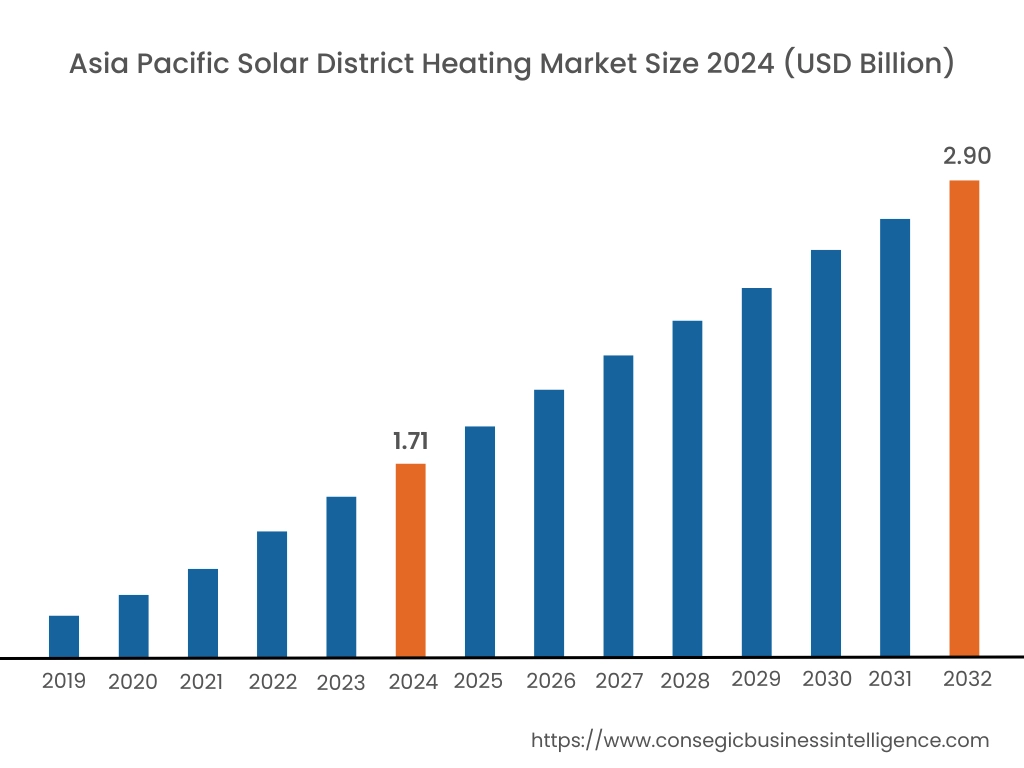
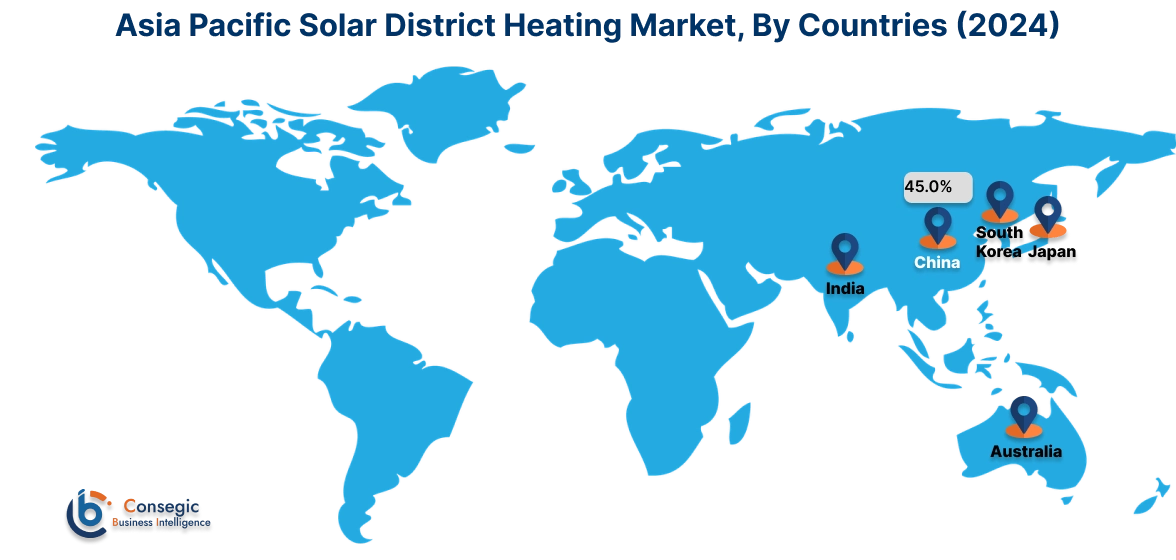
Asia Pacific region was valued at USD 1.71 Billion in 2024. Moreover, it is projected to grow by USD 1.79 Billion in 2025 and reach over USD 2.90 Billion by 2032. Out of this, China accounted for the maximum revenue share of 45.0%. Asia-Pacific is experiencing rapid growth in the solar district heating industry, propelled by rapid urbanization, increasing energy consumption, and climate commitments. China has taken substantial steps in deploying solar thermal systems in residential and industrial clusters, while South Korea and Japan are exploring solar-based heating to reduce dependency on fossil imports. In India, rising environmental awareness and government-backed renewable initiatives are supporting pilot-scale solar heating projects in institutional and urban housing complexes. Analysis of regional trends indicates a growing emphasis on hybrid heating networks that incorporate solar input with centralized control technologies. The positive trend is further supported by favorable climatic conditions and the need for decentralized, clean energy access.
North America is estimated to reach over USD 2.61 Billion by 2032 from a value of USD 1.57 Billion in 2024 and is projected to grow by USD 1.64 Billion in 2025. In North America, solar district heating is gradually expanding, particularly in regions with progressive clean energy goals and cold climates. The United States and Canada are witnessing the rising integration of solar thermal systems into university campuses, municipal networks, and eco-friendly housing developments. Research suggests that while the adoption curve is slower than in Europe, there is rising interest in hybrid systems that combine solar with biomass or geothermal inputs. Strong incentives for renewable energy and net-zero emission targets contribute to a steady uptick in project development, especially in urban areas focused on decarbonizing building heat. The solar district heating market opportunity in North America is rooted in modernizing legacy heating systems and leveraging federal funding for green infrastructure.
Europe dominates the global solar district heating market, bolstered by robust policy support, well-established district energy frameworks, and consistent government investment. Countries like Denmark, Germany, Austria, and Sweden remain pioneers in the integration of large-scale solar thermal fields into municipal heating networks. The region benefits from widespread awareness of renewable heating options and a clear policy alignment with EU decarbonization targets. Market analysis shows that high energy prices and stringent emission reduction mandates are accelerating the adoption of solar-based district heating solutions, especially in retrofitting existing fossil-fueled systems. Furthermore, the development of seasonal thermal energy storage is enhancing system efficiency and flexibility.
- For instance, in December 2024, Serbia received up to €105 Billion in loan from the European Bank for Reconstruction and Development (EBRD) to decarbonize its district heating. This investment will finance the construction of a large-scale solar-thermal power plant in Novi Sad, featuring 38,600 m² of solar collector fields, an 850,000 m³ seasonal heat storage system, a 17 megawatt (MW) heat pump and a 60 MW electric boiler, integrating advanced power-to-heat technology. As part of a clean energy initiative, this project will reduce the natural gas consumption of the district agency by 29%.
In Latin America, the adoption of solar district heating is still at a nascent stage but shows promising potential in countries like Chile, Mexico, and Brazil. The region’s abundant solar resources create favorable conditions for thermal energy capture, especially in remote and off-grid communities. Market analysis suggests that applications in mining, public housing, and tourism infrastructure are opening pathways for solar thermal integration. However, market growth is constrained by limited district heating infrastructure and policy gaps. Efforts to align renewable heat projects with national energy plans and attract foreign investment represent key drivers for regional development.
The Middle East and Africa present a unique context for solar district heating, with significant solar irradiance but relatively limited heating infrastructure in many countries. Nevertheless, high-altitude and high-latitude areas in countries like Turkey, Iran, and South Africa show emerging potential for seasonal heating needs. Analysis highlights that institutional support, pilot programs in urban development, and international partnerships are gradually introducing solar thermal technologies to the region. While adoption is currently limited, long-term growth depends on improving grid integration, financing mechanisms, and technical expertise tailored to regional conditions.
Top Key Players and Market Share Insights:
The solar district heating market is highly competitive with major players providing products and services to the national and international markets. Key players are adopting several strategies in research and development (R&D), product innovation, and end-user launches to hold a strong position in the global solar district heating market. Key players in the solar district heating industry include -
- Aalborg CSP (Denmark)
- Fortum (Finland)
- Göteborg Energi AB (Sweden)
- Kelag Energie & Wärme (Austria)
- Keppel DHCS (Singapore)
- Korea District Heating Corporation (South Korea)
- LOGSTOR A/S (Denmark)
- Ramboll Group (Denmark)
- Savosolar Oyj (Finland)
- Vattenfall AB (Sweden)
Recent Industry Developments :
Acquisitions:
- In 2020, Greenonetec, the largest collector manufacturer in Europe, acquired the Danish-based Arcon-Sunmark, the European leader in developing solar district heating projects. As part of this acquisition, all European Arcon-Sunmark production lines were relocated to Austria/ St.Veit.
Collaborations and Partnerships:
- In August 2024, Pivot Energy announced a 5-year framework agreement with Microsoft to develop up to 500 megawatts (MWac) of community-scale solar energy projects across the United States between 2025 and 2029. This will enable the company to develop approximately 150 U.S. solar projects in roughly 100 communities across 20 states and maximize the benefits of the renewable energy transition at the local level.
Solar District Heating Market Report Insights :
| Report Attributes | Report Details |
| Study Timeline | 2019-2032 |
| Market Size in 2032 | USD 9.52 Billion |
| CAGR (2025-2032) | 6.4% |
| By Capacity |
|
| By Configuration |
|
| By Component |
|
| By Application |
|
| By Region |
|
| Key Players |
|
| North America | U.S. Canada Mexico |
| Europe | U.K. Germany France Spain Italy Russia Benelux Rest of Europe |
| APAC | China South Korea Japan India Australia ASEAN Rest of Asia-Pacific |
| Middle East and Africa | GCC Turkey South Africa Rest of MEA |
| LATAM | Brazil Argentina Chile Rest of LATAM |
| Report Coverage |
|
Key Questions Answered in the Report
How big is the Solar District Heating Market? +
The global Solar District Heating market is estimated to reach over USD 9.52 Billion by 2032 from a value of USD 5.80 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 6.4% from 2025 to 2032.
What specific segmentation details are covered in the Solar District Heating Market report? +
The Solar District Heating market report includes specific segmentation details for capacity, configuration, component and application.
What are the applications in the Solar District Heating Market? +
The applications of the Solar District Heating Market include residential, commercial, industrial, and municipal & district utilities, greenhouse heating, and government institutions.
Who are the major players in the Solar District Heating Market? +
The key participants in the Solar District Heating market are Aalborg CSP (Denmark), Fortum (Finland), Göteborg Energi AB (Sweden), Kelag Energie & Wärme (Austria), Keppel DHCS (Singapore), Korea District Heating Corporation (South Korea), LOGSTOR A/S (Denmark), Ramboll Group (Denmark), Savosolar Oyj (Finland) and Vattenfall AB (Sweden).