- Summary
- Table Of Content
- Methodology
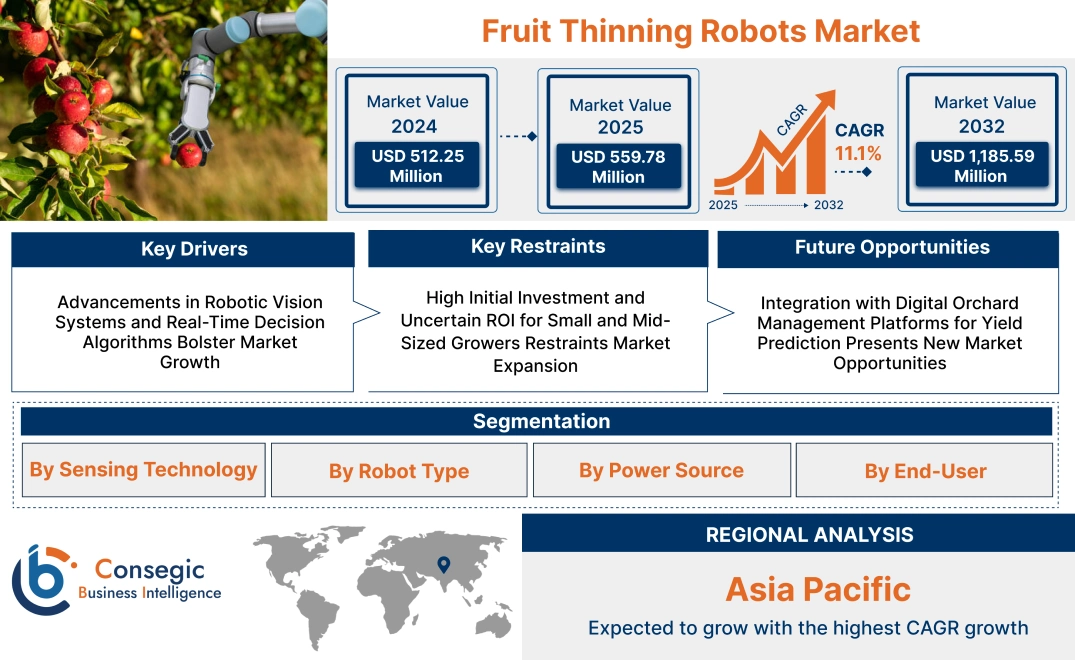
Fruit Thinning Robots Market Size:
Fruit Thinning Robots Market size is estimated to reach over USD 1,185.59 Million by 2032 from a value of USD 512.25 Million in 2024 and is projected to grow by USD 559.78 Million in 2025, growing at a CAGR of 11.1% from 2025 to 2032.
Fruit Thinning Robots Market Scope & Overview:
Fruit thinning robots are semi-autonomous or autonomous machines designed to selectively take away surplus fruit from trees in a way that maximizes yield quality and ensures balanced crop growth. Orchards are where these robots are utilized, using cutting-edge technologies like machine vision, robotic arms, and AI-powered algorithms to locate, evaluate, and remove specific fruit with precision.
Key features are real-time decision-making, GPS-based navigation, and flexible end-effectors for varying tree architecture and fruit types. Their combination facilitates uninterrupted operation, uniform thinning accuracy, and reduced crop damage.
Robots for fruit thinning assist in reducing labor needs, enhancing working efficiency, and promoting even fruit spacing to achieve improved size and ripeness. Their capacity for working on orchard layouts and crop types that vary makes them a worthwhile investment for commercial producers looking to streamline high-value crop management. Integration of automation with smart sensing puts these systems in the category of critical tools for next-generation horticultural processes.
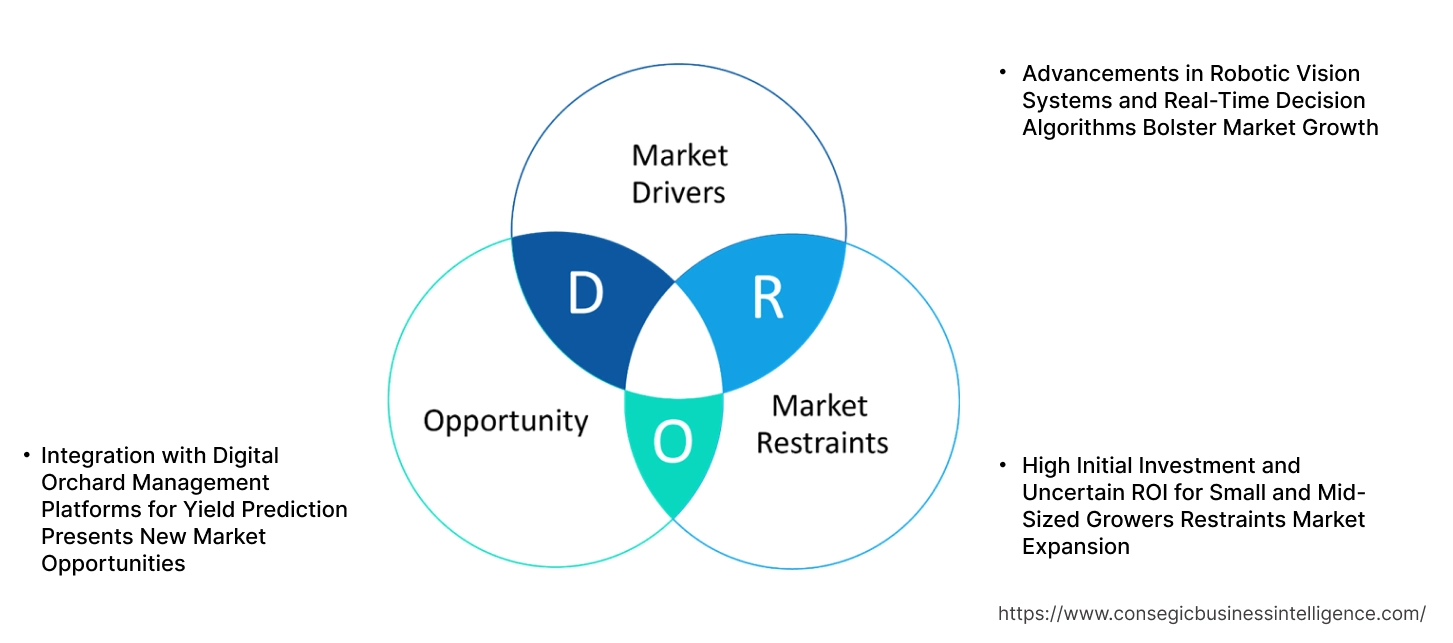
Key Drivers:
Advancements in Robotic Vision Systems and Real-Time Decision Algorithms Bolster Market Growth
Recent developments in computer vision, 3D imaging, and deep learning algorithms are significantly improving the accuracy and efficiency of the thinning robots that previously could not even identify fruit clusters, distinguish viable and excess fruit, and make real-time decisions under variable lighting and canopy conditions. The enhanced robotic arms with multi-axis mobility and precision grip ensure that safe and selective thinning takes place without damaging surrounding fruit or branches. Artificial intelligence-powered software processes intricate orchard data to implement the best thinning routes and minimize the role of human error. Such advancements are becoming more feasible for commercial orchard operations that aim to achieve consistent quality and yield maximization.
- For instance, in March 2024, Orchard Robotics, a startup firm engineering a vehicle-mounted, AI-powered camera system for precision crop management, raised $3.8M across a seed round led by General Catalyst and a pre-seed round led by Contrary. This funding enables the firm to scale up their team and operations to better serve existing and future customers across bigger acreages, while bringing their cutting-edge technology to all parts of the farm. The AI-driven camera is affixed to an available vehicle to collect precise data (including fruit count, size, color, growth rate, and more) about every fruit on every tree to maximize crop yield and quality.
As farmers strive for automation to enhance crop homogeneity and minimize labor, the need for smart and dependable thinning systems is gradually rising, fueling long-term fruit thinning robots market expansion.
Key Restraints:
High Initial Investment and Uncertain ROI for Small and Mid-Sized Growers Restraints Market Expansion
Currently, a significant level of capital investment in purchasing and establishing fruit-thinning robots prohibits entry for the average small or medium-sized orchard operator. Such a project necessitates a major input in capital and requires relatively higher training/maintenance costs combined with possible physical alterations to orchard structures-all added to produce an entry-cost burden. Any acreage considered low or patchy thinning scenarios will continue to make unfavorable return on investments unattainable. Uncertainty about technology lifespan, software maintenance, and availability of service discourages adoption further. In low-labor-cost regions or areas with non-uniform crop production cycles, conventional thinning techniques continue to be economically viable. Although knowledge of benefits from automation is increasing, economic risk and absence of scale still restrain accessibility for most of the market—thus limiting the fruit thinning robots market growth even as demand increases.
Future Opportunities :
Integration with Digital Orchard Management Platforms for Yield Prediction Presents New Market Opportunities
The coupling of fruit thinning robots with software orchard management platforms is unveiling new opportunities in yield prediction and agronomic decision-making. During thinning tasks, as the robots gather fruit number, size, and spatial distribution data, they are inputs to centralized computer programs that develop real-time yields predictions and insights into tree health. These software platforms enable farmers to plan for harvest logistics, irrigate and optimize, and input applications more precisely. Demand for data-driven orchard management is growing among high-value fruit growers looking to enhance profitability and achieve certification requirements. The capacity to integrate robotic thinning with more comprehensive orchard analytics and traceability systems is enhancing the value proposition of automation.
- For instance, OnePlanet, a collaboration between Wageningen University & Research, Radboud University, Radboudumc, and imec, launched the "Digital Orchard" research programme to develop technology for autonomous pruning robots trained on digital twins of the trees in orchards to ensure data-driven decision making for harvests.
This intersection of robotics and digital agriculture is developing scalable solutions for precision horticulture, unleashing robust fruit thinning robots market opportunities driven by both necessity and expansion.
Fruit Thinning Robots Market Segmental Analysis :
By Sensing Technology:
Based on sensing technology, the market is categorized into vision-based (2D imaging, 3D imaging, hyperspectral imaging), non-vision-based (mechanical sensing, LiDAR), and others.
The vision-based systems accounted for the largest revenue share in 2024.
- Vision-based fruit thinning robots utilize advanced imaging technologies such as RGB cameras, hyperspectral imaging, and 2D & 3D vision systems to identify fruit clusters and assess spacing requirements.
- These systems are integrated with machine learning algorithms to distinguish between fruits and leaves, analyze maturity levels, and execute precision thinning actions.
- Vision-based systems are widely used in apple, peach, and citrus orchards where high selectivity is crucial for maximizing yield quality.
- As per the fruit thinning robots market analysis, the dominance of vision systems reflects their high accuracy and adaptability across various tree geometries and canopy densities.
The non-vision-based sensing is expected to witness the fastest CAGR during the forecast period.
- Non-vision-based sensing technologies include LiDAR, mechanical sensors, and ultrasonic devices, which are increasingly adopted for canopy profiling and obstacle detection.
- These systems are particularly useful in low-light or dusty conditions where vision sensors may fail or be less reliable.
- Integration of non-vision sensors enhances the spatial awareness of autonomous robots, enabling more consistent thinning operations across varied orchard environments.
- As per the leading fruit thinning robots market trends, the increasing focus on rugged, all-weather robotic performance is driving rapid adoption of non-vision-based sensing solutions.
By Robot Type:
Based on robot type, the market is segmented into autonomous robots and semi-autonomous robots.
The autonomous robots segment held the largest fruit thinning robots market share in 2024.
- Autonomous systems perform thinning tasks independently using machine vision, robotic arms, and self-navigation modules.
- They reduce labor costs and improve efficiency by operating continuously with minimal human oversight.
- These robots are increasingly adopted in large-scale orchards seeking long-term operational cost savings.
- As per the fruit thinning robots market analysis, autonomous systems are leading the market due to rising investments in fully automated field solutions.
The semi-autonomous robots segment is projected to grow steadily during the forecast period.
- Semi-autonomous robots combine robotic manipulation with human-in-the-loop control, offering more flexibility in complex terrain.
- These systems are preferred by mid-sized farms that require some level of operator intervention, especially during peak seasons.
- Lower upfront cost and simpler calibration make them attractive for new adopters in the agri-tech sector.
- According to fruit thinning robots market trends, hybrid models are being developed to support dynamic transitions between manual and autonomous modes.
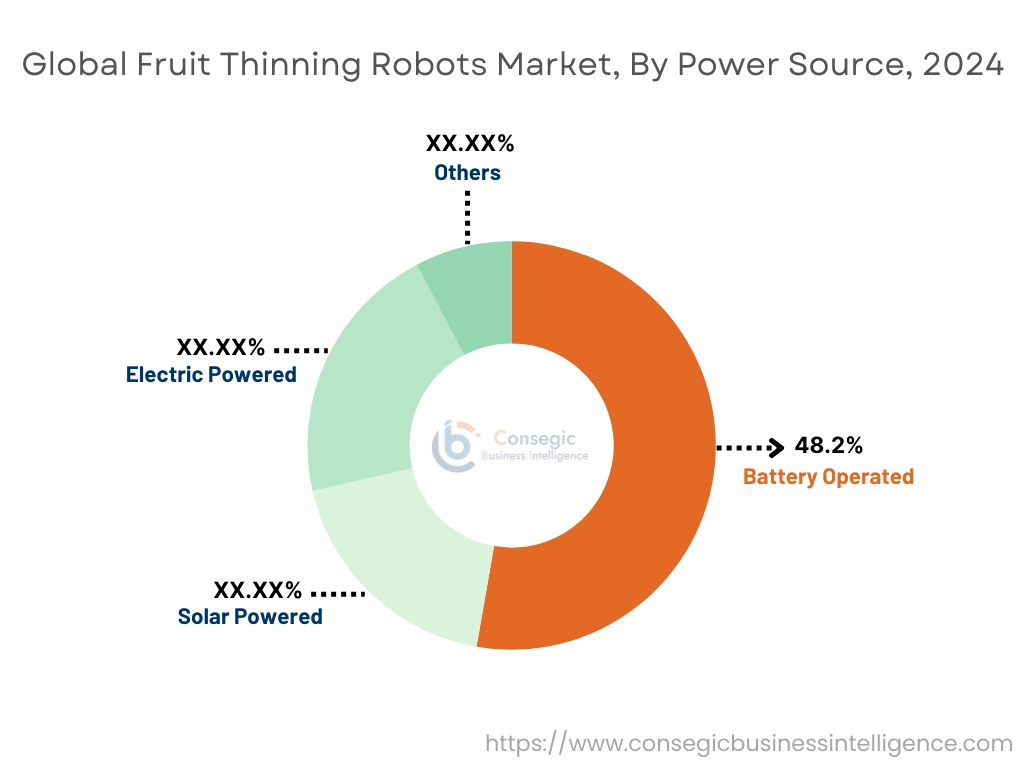
By Power Source:
Based on power source, the market is segmented into electric powered, solar powered, battery operated, and others.
The battery operated segment held the largest fruit thinning robots market share of 48.2% in 2024.
- Battery-powered fruit thinning robots are popular due to their portability, zero emissions, and compatibility with remote or off-grid orchards.
- Advancements in lithium-ion battery technologies have extended operational time and reduced charging intervals.
- These systems are widely used in orchard settings where silent operation and maneuverability are essential.
- The battery-powered models contribute to the rise in fruit thinning robots market demand due to their reliability and ease of deployment.
The solar powered segment is projected to witness the fastest CAGR during the forecast period.
- Solar-powered robots offer long-term cost efficiency and sustainability benefits, especially in sunny agricultural regions.
- These units reduce the carbon footprint and align with eco-conscious farming practices gaining traction globally.
- Integration of solar panels on mobile platforms enables continuous energy input and extended field coverage.
- Fruit thinning robots market expansion is supported by increasing incentives for clean-energy agricultural equipment.
By End-User:
Based on end user, the fruit thinning robots market is segmented into individual farmers, agricultural cooperatives, corporate farming enterprises, greenhouses, research institutes, and others.
The corporate farming enterprises segment accounted for the largest revenue share in 2024.
- Large-scale commercial farms adopt thinning robots to improve productivity, reduce reliance on manual labor, and maintain consistent fruit quality.
- These farms typically invest in high-end autonomous systems and integrate them with centralized farm management software.
- Customization, fleet control, and remote diagnostics are key features demanded in this segment.
- The fruit thinning robots market demand from commercial enterprises is driven by the need to meet export-grade crop uniformity and efficiency goals.
The greenhouses segment is anticipated to grow at the fastest CAGR over the forecast period.
- Greenhouse operations increasingly employ robotic thinning to handle high-density fruit cultivars in controlled environments.
- Compact, modular robots are preferred in these setups to navigate narrow aisles and delicate plant arrangements.
- Robots with multispectral and hyperspectral sensors enable precise monitoring of fruit clusters and thinning conditions.
- Greenhouse adoption is increasing due to high ROI in climate-sensitive crop production, driving fruit thinning robots market growth.
Regional Analysis:
The regions covered are North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, the Middle East and Africa, and Latin America.
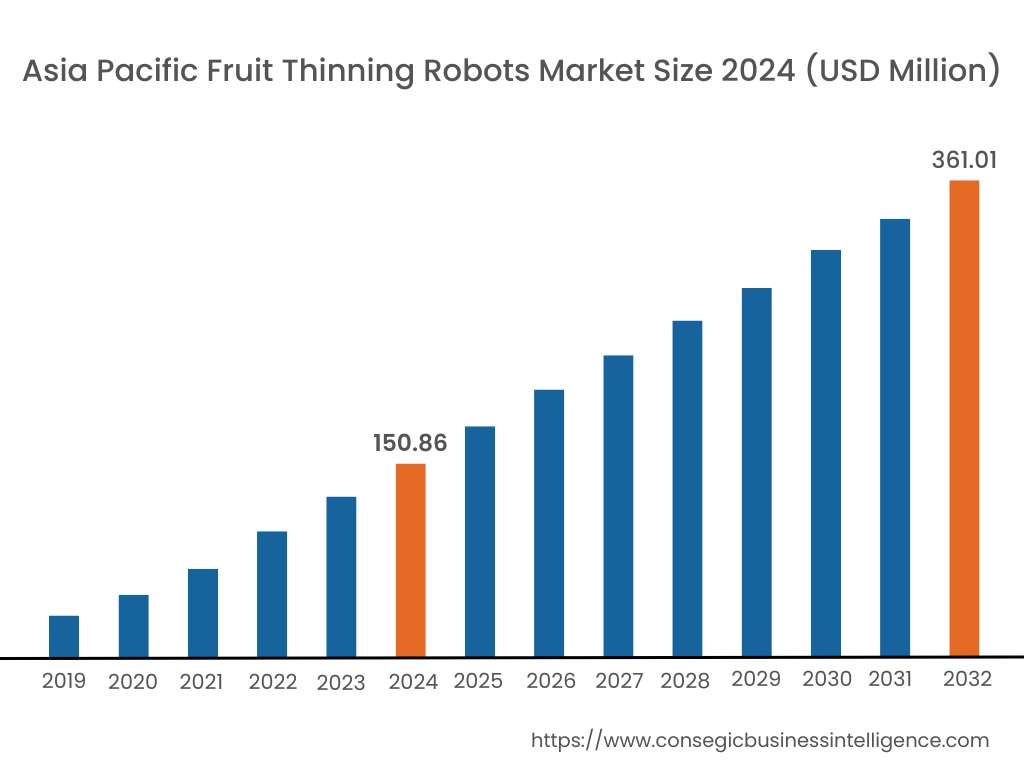
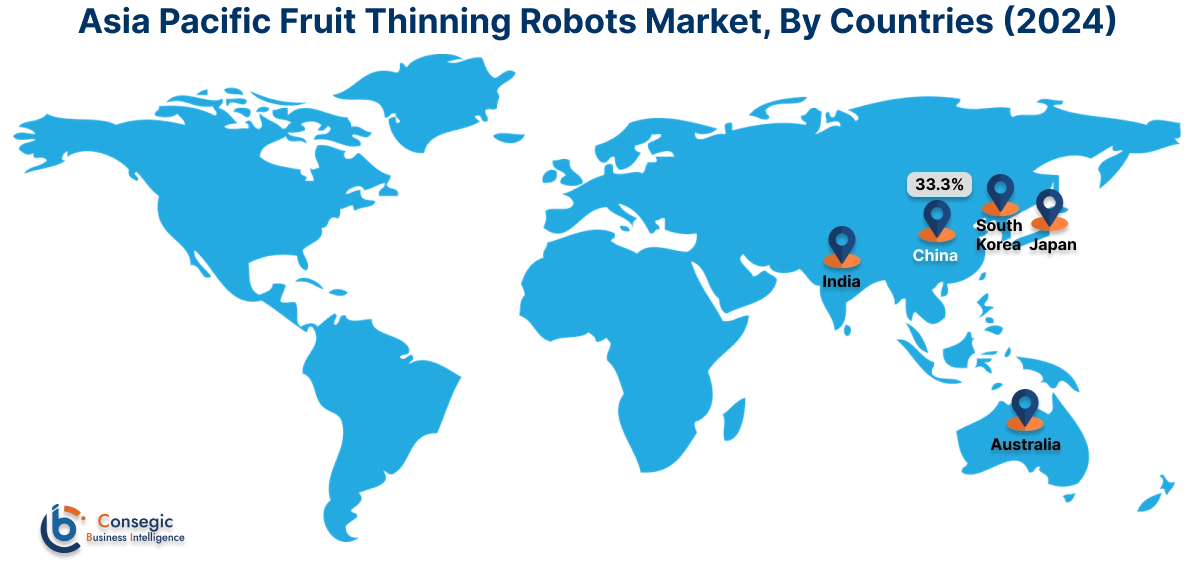
Asia Pacific region was valued at USD 150.86 Million in 2024. Moreover, it is projected to grow by USD 165.33 Million in 2025 and reach over USD 361.01 Million by 2032. Out of this, China accounted for the maximum revenue share of 33.3%. The Asia-Pacific region is a high-potential region with interest in agricultural robotics increasing rapidly, most notably in Japan, South Korea, China, and Australia. South Korea and Japan are early movers, capitalizing on their high-end robotics production capabilities and scarce rural labor supply. Market research points out that government-funded automation initiatives and subsidies for precision farming are driving investments in robotic technology for apple, pear, and persimmon orchards. Domestic innovation and demand for intelligent agriculture solutions in dense fruit-growing areas are pushing momentum in China. The fruit thinning robots market opportunity in Asia-Pacific is further driven by the increasing relevance of export-grade fruit, requiring uniform ripeness and consistent size.
North America is estimated to reach over USD 384.25 Million by 2032 from a value of USD 169.92 Million in 2024 and is projected to grow by USD 185.33 Million in 2025. North America is one of the most dynamic areas for the deployment and development of automated orchard systems. The United States, especially in fruit states such as Washington and California, is embracing robotic thinning technology to overcome seasonal labor shortages and enhance orchard yields. Market analysis shows strong institutional backing for automation in specialty crop production, with pilot programs and large-scale trials being undertaken by forward-thinking growers. The incorporation of machine vision and AI-enabled sensors into robot arms is improving thinning precision on apple, peach, and citrus groves. Long-term growth depends on the development of autonomous field alignment and navigation and aligning with sustainable agriculture objectives.
Europe offers a regulation-oriented and innovation-based climate in which the transition to low-labor, high-precision horticulture is fueling automation in perennial fruit farming. Italy, France, and Spain, among other countries, are investing in orchard robots to enhance productivity and counter labor availability challenges. Adoption has been mostly focused in apple orchards and vineyards, where intensive thinning is important for market quality and acceptance. There is also a focus on environmental conservation and lower agrochemical usage that favors applications of robots that can selectively thin without contaminating nearby crops. Partnerships between agri-tech startups and research centers are increasingly scaling deployment on small to medium-sized farms.
Latin America illustrates slow uptake, with nations such as Chile, Brazil, and Argentina starting to invest in robotics for labor-intensive tasks. Market research indicates that while big farms drive commercial production of fruit, variable labor supply and rising labor expenses are driving enthusiasm for automation. Pilot tests and small-scale pilot implementations are currently in focus for high-value crops such as grapes and apples. The region's diverse terrain and limited robotics infrastructure pose challenges, but technological alliances and government modernization initiatives may unlock future potential. Expansion in this region is likely to intensify as awareness grows and unit costs fall.
In the Middle East and Africa, adoption is still at an early stage, but demand for efficiency in farm operations is slowly growing. In nations like South Africa, Israel, and some regions of the UAE, orchards are looking for new ways to maximize thinning, particularly in light of water constraints and manpower shortages. Market research identifies Israel as a leader with its developed agri-tech industry and sophisticated field test facilities. In sub-Saharan Africa, the industry of fruit thinning robots is yet in its nascency, although there is growing interest through donor-funded modernization drives to increase horticultural exports and promote uniformity in crops.
Top Key Players and Market Share Insights:
The fruit thinning robots market is highly competitive with major players providing products and services to the national and international markets. Key players are adopting several strategies in research and development (R&D), product innovation, and end-user launches to hold a strong position in the global fruit thinning robots market. Key players in the fruit thinning robots industry include -
- Kubota Corporation (Japan)
- Naïo Technologies (France)
- Bakus Robotics (USA)
- Abundant Robotics (USA)
- Traptic (USA)
- Octinion (Belgium)
- Ripe Robotics (Australia)
- Dogtooth Technologies (United Kingdom)
- AGROBOT (Spain)
- Harvest CROO Robotics LLC (USA)
Recent Industry Developments :
Acquisitions:
- In April 2025, Taylor Farms, the California-based ready-to-eat salad company, acquired FarmWise, an agricultural technology robotics company providing precision weeding and thinning solutions. This highlights Taylor Farms’ objective to improve agricultural technology and sustainable farming practices as well as deliver high-quality produce to its customers. Furthermore, this decision aligns with the company’s long-term goal of adopting advanced technologies that benefit the industry at large.
- In March 2025, the vertical farming company Oishii, known for its premium strawberries and tomatoes, acquired the harvest robotics startup Tortuga AgTech. Tortuga AgTech developed robots to harvest strawberries, table grapes, and berries, as well as collect data from plants and perform other tasks such as trimming and treating plants with UV-C light. This decision enables the companies to remain at the forefront of agricultural innovation, build stronger infrastructure, and strive for advancement in the sector.
Partnerships:
- In May 2023, Tevel partnered with Unifrutti to expand its presence in Chile, South America.
Fruit Thinning Robots Market Report Insights:
| Report Attributes | Report Details |
| Study Timeline | 2019-2032 |
| Market Size in 2032 | USD 1,185.59 Million |
| CAGR (2025-2032) | 11.1% |
| By Sensing Technology |
|
| By Robot Type |
|
| By Power Source |
|
| By End-User |
|
| By Region |
|
| Key Players |
|
| North America | U.S. Canada Mexico |
| Europe | U.K. Germany France Spain Italy Russia Benelux Rest of Europe |
| APAC | China South Korea Japan India Australia ASEAN Rest of Asia-Pacific |
| Middle East and Africa | GCC Turkey South Africa Rest of MEA |
| LATAM | Brazil Argentina Chile Rest of LATAM |
| Report Coverage |
|
Key Questions Answered in the Report
How big is the Fruit Thinning Robots Market? +
Fruit Thinning Robots Market size is estimated to reach over USD 1,185.59 Million by 2032 from a value of USD 512.25 Million in 2024 and is projected to grow by USD 559.78 Million in 2025, growing at a CAGR of 11.1% from 2025 to 2032.
What specific segmentation details are covered in the Fruit Thinning Robots Market report? +
The Fruit Thinning Robots market report includes specific segmentation details for sensing technology, robot type, power source and end-user.
What are the end-users of the Fruit Thinning Robots Market? +
The end-users of the Fruit Thinning Robots Market are individual farmers, agricultural cooperatives, corporate farming enterprises, greenhouses, research institutes, and others.
Who are the major players in the Fruit Thinning Robots Market? +
The key participants in the Fruit Thinning Robots market are Kubota Corporation (Japan), Naïo Technologies (France), Octinion (Belgium), Ripe Robotics (Australia), Dogtooth Technologies (United Kingdom), AGROBOT (Spain), Harvest CROO Robotics LLC (USA), Bakus Robotics (USA), Abundant Robotics (USA) and Traptic (USA).