- Summary
- Table Of Content
- Methodology
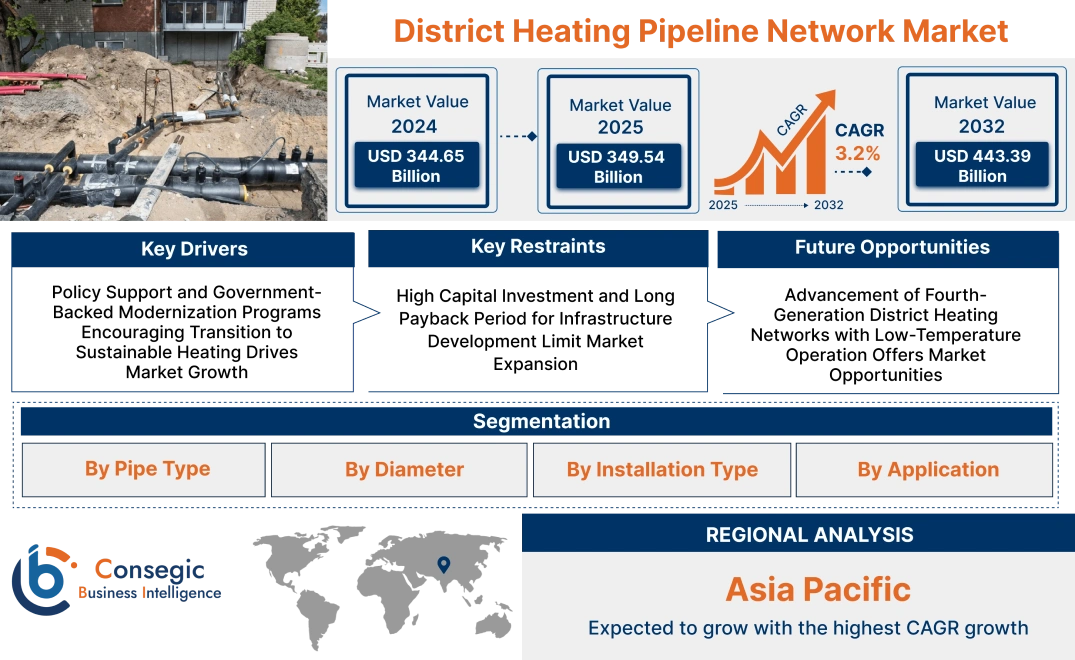
District Heating Pipeline Network Market Size:
District Heating Pipeline Network Market size is estimated to reach over USD 443.39 Billion by 2032 from a value of USD 344.65 Billion in 2024 and is projected to grow by USD 349.54 Billion in 2025, growing at a CAGR of 3.2% from 2025 to 2032.
District Heating Pipeline Network Market Scope & Overview:
District heating pipeline network is an underground infrastructure system that is used to carry thermal energy in the form of hot water or steam from centralized heat sources to residential, commercial, or industrial buildings. The networks facilitate efficient, large-scale distribution of heating produced from sources like combined heat and power plants, biomass, or waste-to-energy plants.
The pipeline systems generally consist of pre-insulated steel or polymer pipes, leak detection equipment, expansion compensators, and control valves. Designed for high durability, thermal insulation, and corrosion resistance, they minimize heat loss and operational life.
District heating pipeline network enables centralized management, lower emissions, and optimal utilization of energy in urban settings. It enables scalability, incorporation of renewable energies, and upgradation of aging heating infrastructure. Its contribution to increased energy efficiency and reliable thermal distribution makes it an essential element in sustainable urban energy planning and long-term infrastructure development.
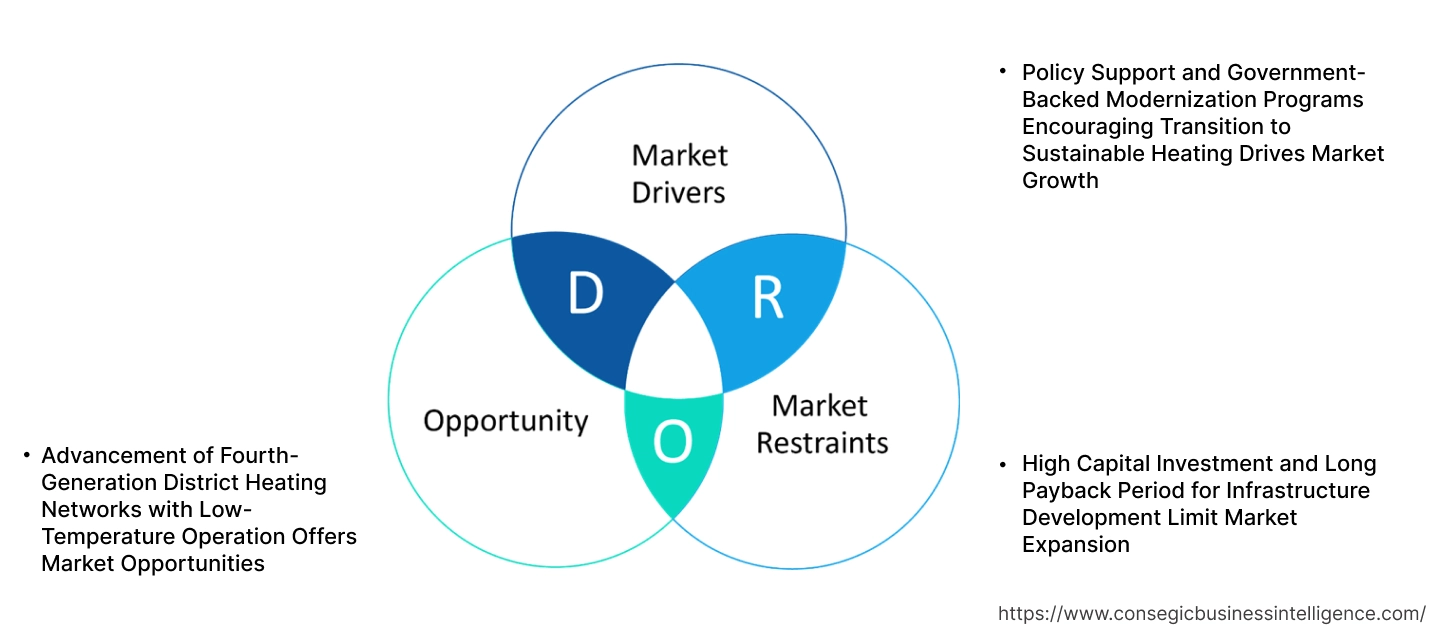
Key Drivers:
Policy Support and Government-Backed Modernization Programs Encouraging Transition to Sustainable Heating Drives Market Growth
Governments in Europe, Asia, and North America are rolling out focused programs to encourage sustainable district heating infrastructure. These initiatives involve direct subsidies, green energy incentives, and compulsory mandates for phasing out fossil-fueled heat supply in favor of renewable and waste heat integration. National policies on climate action and energy transition are focusing on the replacement of old, inefficient pipelines with low-loss, pre-insulated networks for high-efficiency and low-emission distribution. This policy momentum is being met by municipal utilities and private operators upgrading pipeline infrastructure to the new thermal performance and reliability requirements. These public-private funding streams are increasing system efficiency and making the decarbonization of urban heating over the long term possible.
- For instance, Hamburg, a German city, is undergoing a significant energy transition with the financial support from the Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Climate Action (BMWK) and KfW. In January 2025, Aurubis AG and Hamburger Energiewerke completed a new exhaust heat project using the approved funding. The support enabled Aurubis to complete the necessary plant conversion, heat extraction and internal pipeline up to the site perimeter cost-effectively, allowing its waste heat to feed into the 860 km long district heating network.
With regulatory frameworks leading to ongoing environmental compliance and energy resilience, the demand for next-generation district heating infrastructure is increasing, leading to ongoing district heating pipeline network market expansion.
Key Restraints:
High Capital Investment and Long Payback Period for Infrastructure Development Limit Market Expansion
Building or expanding district heating pipe networks entails significant investment in excavation, insulation, hydraulic balance systems, and control infrastructure. Installation in heavily populated cities comes with additional costs for underground utility coordination, traffic disruption, and land access negotiations. Although the systems provide long-term energy and emissions savings, the up-front investment is high, with a payback period that frequently runs longer than a decade. This causes funding difficulties for municipalities and private operators, particularly in areas lacking robust policy stimuli or beneficial tariff regimes. Low heating density cities and towns experience it as economically impossible to launch full-fledged network roll-outs. Even in cities, investment for the upgrading of existing networks is frequently postponed owing to budget limitations. Even with increasing demand for sustainable thermal infrastructure, such capital-intensive needs still hold back district heating pipeline network market growth.
Future Opportunities :
Advancement of Fourth-Generation District Heating Networks with Low-Temperature Operation Offers Market Opportunities
Fourth-generation district heating networks are optimized for reduced operating temperatures, enhancing system efficiency and compatibility with ambient and renewable heat sources. The systems minimize heat loss, reduce material stress, and facilitate integration with solar thermal, geothermal, and industrial waste heat. Low-temperature network transition requires adaptable, corrosion-free pipes with excellent insulation performance and intelligent control functionality. These systems also improve end-user safety and enable decentralized heat producers and prosumers to be connected. As urban areas decarbonize and invest in net-zero energy infrastructure, the need for low-temperature, modular pipeline networks is increasing. Development in mixed-use developments, energy-positive neighborhoods, and climate-neutral urban proposals is strengthening the demand for flexible and future-proof heating grids. Producers offering low-loss piping, hydraulic balancing technologies, and digital integration are best placed to meet this shift—unlocking long-term district heating pipeline network market opportunities in line with sustainable urban development.
District Heating Pipeline Network Market Segmental Analysis :
By Pipe Type:
Based on pipe type, the market is segmented into pre-insulated steel pipes, polymer pipes, and others.
The pre-insulated steel pipes segment accounted for the largest district heating pipeline network market share in 2024.
- Pre-insulated steel pipes are preferred for their high thermal resistance, mechanical strength, and long service life in high-temperature systems.
- These pipes are widely used in large-scale district heating systems, particularly in urban and cold-climate regions.
- Their robust insulation reduces heat loss over long distances, improving overall system efficiency.
- For instance, in July 2024, REHAU launched the new standard in pre-insulated pipe, RAUVIPEX. This pipe offers high flexibility, low heat losses, and an innovative longitudinal watertightness barrier. The integration of newly developed fine-pored PUR foam in its structures ensures an optimum insulation performance and improved bending elasticity. Furthermore, the flexibility enables easier installation.
- As per district heating pipeline network market analysis, they remain the backbone of most centralized heating networks.
The polymer pipes segment is projected to witness the fastest CAGR during the forecast period.
- Polymer pipes, including cross-linked polyethylene (PEX) and polybutylene (PB), offer corrosion resistance, light weight, and easier installation.
- These pipes are increasingly adopted in low-temperature and small-scale heating networks, especially in residential developments.
- Their flexibility reduces installation labor and material costs, especially in retrofit and modular applications.
- According to district heating pipeline network market trends, the shift toward low-carbon and distributed heating solutions is boosting demand for polymer-based piping.
By Diameter:
Based on diameter, the district heating pipeline network market is segmented into 25–100 mm, 101–300 mm, and ≥300 mm.
The 101–300 mm segment accounted for the largest revenue share in 2024.
- Pipes in this range are commonly used in mid-scale municipal and commercial district heating systems.
- They strike a balance between flow capacity and thermal efficiency, making them ideal for urban district heating distribution.
- This diameter is also compatible with most pre-insulated steel and flexible polymer piping solutions.
- As per district heating pipeline network market analysis, growing urbanization and energy retrofits support segment stability.
The ≥300 mm segment is expected to register the fastest CAGR over the forecast period.
- Larger diameter pipelines are used for high-capacity transmission lines from central heat plants to substations or large industrial consumers.
- These systems are critical in capital cities and densely populated districts where heat must be delivered over long distances.
- Advancements in joint insulation and trenchless installation methods are enhancing the feasibility of large-diameter systems.
- District heating pipeline network market trends indicate increased investment in long-haul infrastructure as utilities modernize legacy grids.
By Installation Type:
Based on installation type, the district heating pipeline network market is divided into overground and underground.
The underground segment held the largest revenue share in 2024.
- Underground installation is the most common method due to safety, aesthetic, and weather protection advantages.
- It ensures minimal heat loss and prevents mechanical damage, particularly in urban and public areas.
- Modern underground systems incorporate leak detection, corrosion protection, and smart monitoring technologies.
- Additionally, buried networks are preferred for long-term energy planning and climate resilience, and the convenience provided to citizens drives the district heating pipeline network market demand.
The overground segment is projected to experience fastest CAGR during the forecast period.
- Overground pipelines are favored in industrial zones and temporary heating projects due to ease of inspection and lower installation costs.
- These systems are often deployed in areas with challenging soil conditions or where rapid expansion is needed.
- Overground installations support modular expansion and repairs without disrupting urban infrastructure.
- District heating pipeline network market expansion in industrial parks and export-oriented economic zones supports this segment.
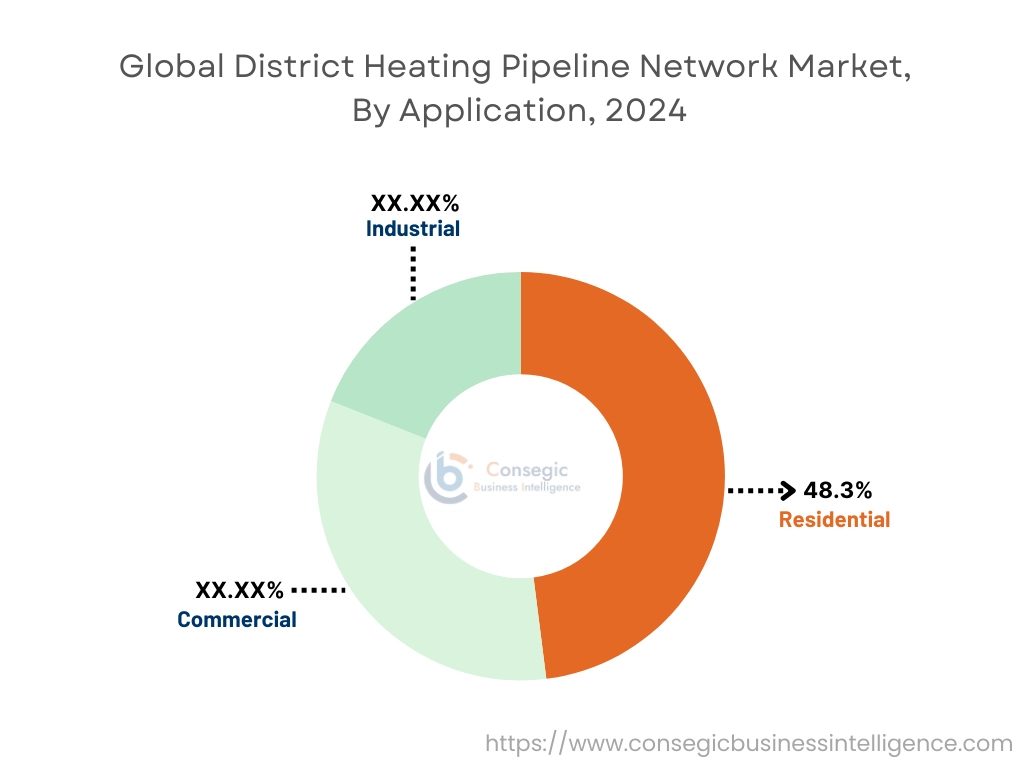
By Application:
Based on application, the market is segmented into residential, commercial, and industrial.
The residential segment accounted for the largest district heating pipeline network market share of 48.3% in 2024.
- Residential district heating networks supply space heating and domestic hot water to single-family homes, apartment blocks, and housing cooperatives.
- These systems are widespread in Northern and Eastern Europe, supported by government policies and retrofitting programs.
- Smart metering and user-level temperature control are improving efficiency and user satisfaction.
- District heating pipeline network market demand in this segment is driven by urban redevelopment and energy-efficient building mandates.
The industrial segment is projected to grow at the fastest CAGR during the forecast period.
- Industrial applications use district heating for process steam, space heating, and waste heat recovery.
- Large industrial users often act as both heat consumers and contributors, enabling circular energy models.
- Adoption is increasing in the paper, chemical, and food processing sectors with high thermal energy requirements.
- Furthermore, industry decarbonization targets are driving infrastructure upgrades in this segment, propelling district heating pipeline network market growth.
Regional Analysis:
The regions covered are North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, the Middle East and Africa, and Latin America.
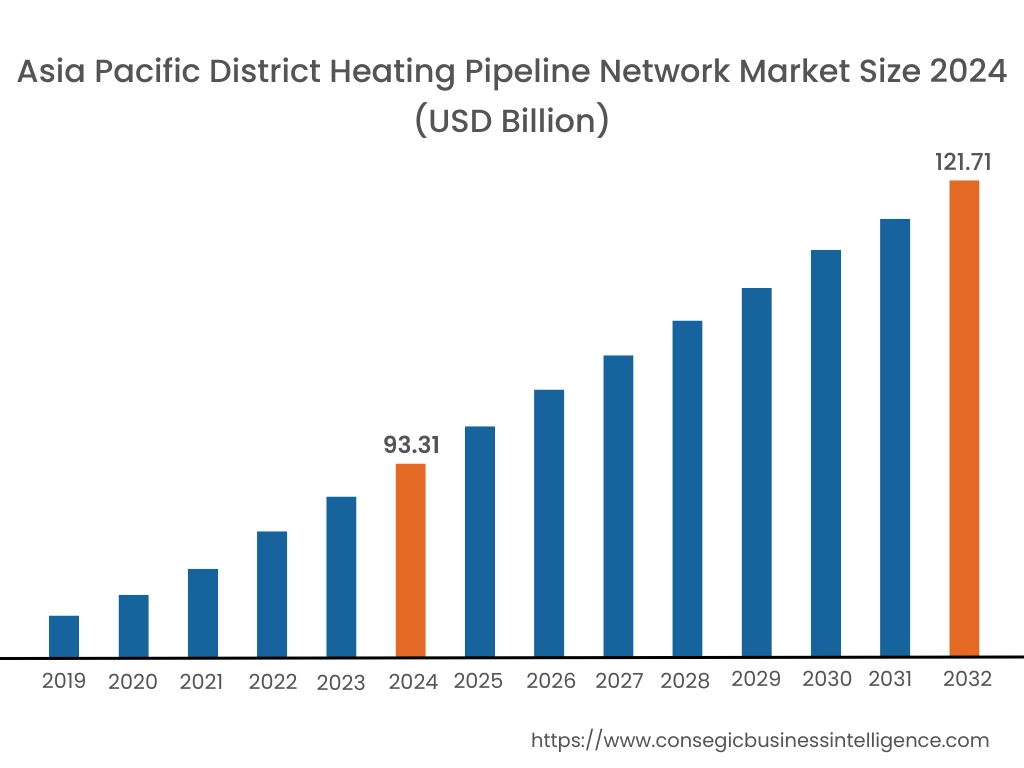
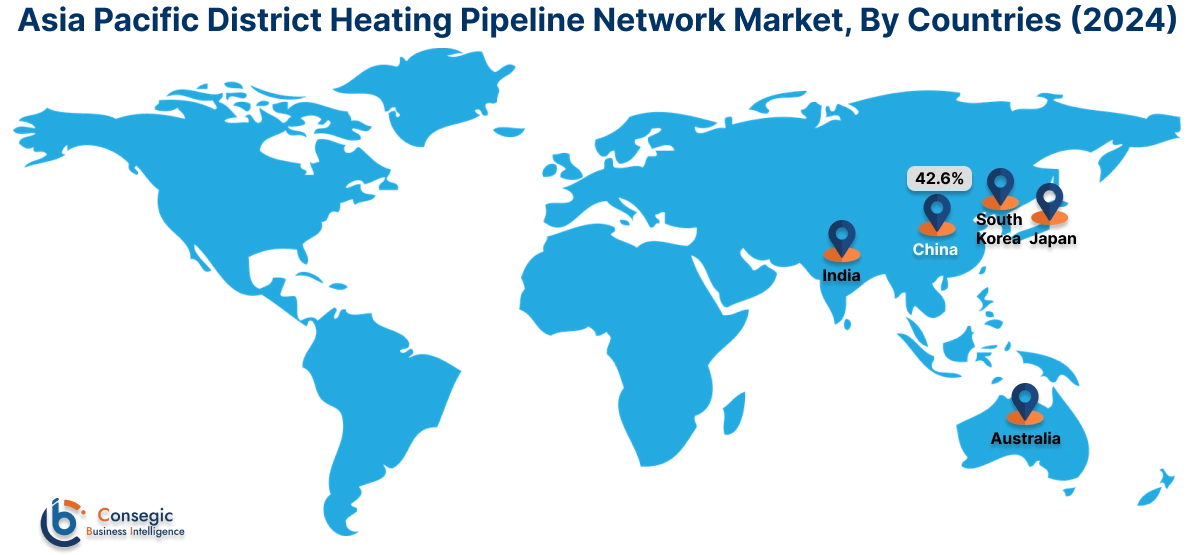
Asia Pacific region was valued at USD 93.31 Billion in 2024. Moreover, it is projected to grow by USD 94.74 Billion in 2025 and reach over USD 121.71 Billion by 2032. Out of this, China accounted for the maximum revenue share of 42.6%. The Asia-Pacific region is witnessing strong expansion, especially in South Korea, China, and Japan, where compact urban centers and harsh seasonal conditions boost the need for centralized heat solutions. Market research shows major investment in pipeline upgrading in north China with the aid of national clean heating policies and coal-to-gas conversion schemes. In South Korea, upgrading of outdated systems and integrating them with smart city schemes are making it possible to have increased energy utilization efficiency. Japan, while constrained by coverage of pipelines, is also trying combined heat and power (CHP)-assisted district heating in certain urban areas. Growing recognition of energy security and air pollution management remains driving governments to develop district energy infrastructure further across the region.
North America is estimated to reach over USD 147.69 Billion by 2032 from a value of USD 114.58 Billion in 2024 and is projected to grow by USD 116.23 Billion in 2025. In North America, the district heating pipeline network industry is going through steady modernization, especially in areas concentrated on sustainable urban development. The United States and Canada are increasing such systems in university campuses, hospital complexes, and central business districts, where centralized energy supply improves operational efficiency. Market analysis points to a growing trend toward incorporating renewable heat sources like biomass, geothermal, and recovered waste heat into existing pipeline infrastructure. Expansion in the region is underpinned by city-driven decarbonization measures and thermal network upgrades to improve energy efficiency and cold climate resilience. Smart thermal metering and pre-insulated pipe investments are increasing system efficiency and minimizing heat losses in city networks.
Europe leads the world in district heating penetration, fueled by ambitious energy transformation targets, coal and gas phase-outs, and high building energy efficiency standards. Denmark, Germany, Sweden, and the Netherlands are all actively expanding and upgrading district heating pipeline systems to accommodate integration of renewables and low-temperature distribution systems. Market intelligence demonstrates that government incentives and emission-based incentives are driving upgrades of legacy high-loss pipelines with flexible, corrosion-resistant piping. Moreover, the impetus for sector coupling—electricity, heat, and transport sector integration—only serves to increase the thermal network contribution to overall energy planning. The European district heating pipeline network market opportunity keeps expanding as municipalities grow climate-neutral city development initiatives.
Latin America showcases a developing district heating pipeline network market, with selective application in Chile and Argentina. Market research indicates that uptake is mainly in commercial and institutional buildings in colder high-altitude areas where centralized heating offers energy and cost benefits. While natural gas remains the most prominent regional heat source, the shift towards sustainable energy planning provides opportunities for developing thermal networks in urban areas. Integrating scalable, modular pipeline systems into new clusters of smart buildings and industrial parks, backed by renewable heat supply and foreign capital, offers new market opportunities.
In the Middle East and Africa, district heating systems are in their infancy but slowly picking up interest, especially in high-density city developments or industrial thermal energy demand in certain countries. In markets like Turkey, UAE, and South Africa, market research points towards developing applications in mixed-use development, hospitality areas, and green cities developments. The focus on enhancing energy efficiency and minimizing dependence on decentralized systems is driving exploration for district heating solutions. Climatic factors and limited regulatory backing continue to pose adoption hurdles, nonetheless. Long-term growth opportunities are underpinned by integrated infrastructure planning and interest in diversifying energy systems to incorporate waste heat recovery as well as geothermal integration.
Top Key Players and Market Share Insights:
The district heating pipeline network market is highly competitive with major players providing products and services to the national and international markets. Key players are adopting several strategies in research and development (R&D), product innovation, and end-user launches to hold a strong position in the global district heating pipeline network market. Key players in the district heating pipeline network industry include -
- Fortum Corporation (Finland)
- Vattenfall AB (Sweden)
- REHAU (Germany)
- Uponor Corporation (Finland)
- ISOPLUS Group (Austria)
- ENGIE (France)
- Danfoss (Denmark)
- Statkraft AS (Norway)
- LOGSTOR Denmark Holding ApS (Denmark)
- Vital Energi Ltd. (United Kingdom)
Recent Industry Developments :
Acquisitions:
- In March 2021, Partners Group acquired one of the largest district heating platforms (the "District Heating Platform" or "the Company") in the Baltics from Finnish energy company Fortum Corporation ("Fortum"). The Company operated in Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania, and generated heat capacity of 881MW and power capacity of 130MV.
District Heating Pipeline Network Market Report Insights:
| Report Attributes | Report Details |
| Study Timeline | 2019-2032 |
| Market Size in 2032 | USD 443.39 Billion |
| CAGR (2025-2032) | 3.2% |
| By Pipe Type |
|
| By Diameter |
|
| By Installation Type |
|
| By Application |
|
| By Region |
|
| Key Players |
|
| North America | U.S. Canada Mexico |
| Europe | U.K. Germany France Spain Italy Russia Benelux Rest of Europe |
| APAC | China South Korea Japan India Australia ASEAN Rest of Asia-Pacific |
| Middle East and Africa | GCC Turkey South Africa Rest of MEA |
| LATAM | Brazil Argentina Chile Rest of LATAM |
| Report Coverage |
|
Key Questions Answered in the Report
How big is the District Heating Pipeline Network Market? +
District Heating Pipeline Network Market size is estimated to reach over USD 443.39 Billion by 2032 from a value of USD 344.65 Billion in 2024 and is projected to grow by USD 349.54 Billion in 2025, growing at a CAGR of 3.2% from 2025 to 2032.
What specific segmentation details are covered in the District Heating Pipeline Network Market report? +
The District Heating Pipeline Network market report includes specific segmentation details for pipe type, diameter, installation type and application.
What are the applications of the District Heating Pipeline Network Market? +
The application of the District Heating Pipeline Network Market are residential, commercial, and industrial.
Who are the major players in the District Heating Pipeline Network Market? +
The key participants in the District Heating Pipeline Network market are Fortum Corporation (Finland), Vattenfall AB (Sweden), ENGIE (France), Danfoss (Denmark), Statkraft AS (Norway), LOGSTOR Denmark Holding ApS (Denmark), Vital Energi Ltd. (United Kingdom), REHAU (Germany), Uponor Corporation (Finland) and ISOPLUS Group (Austria).